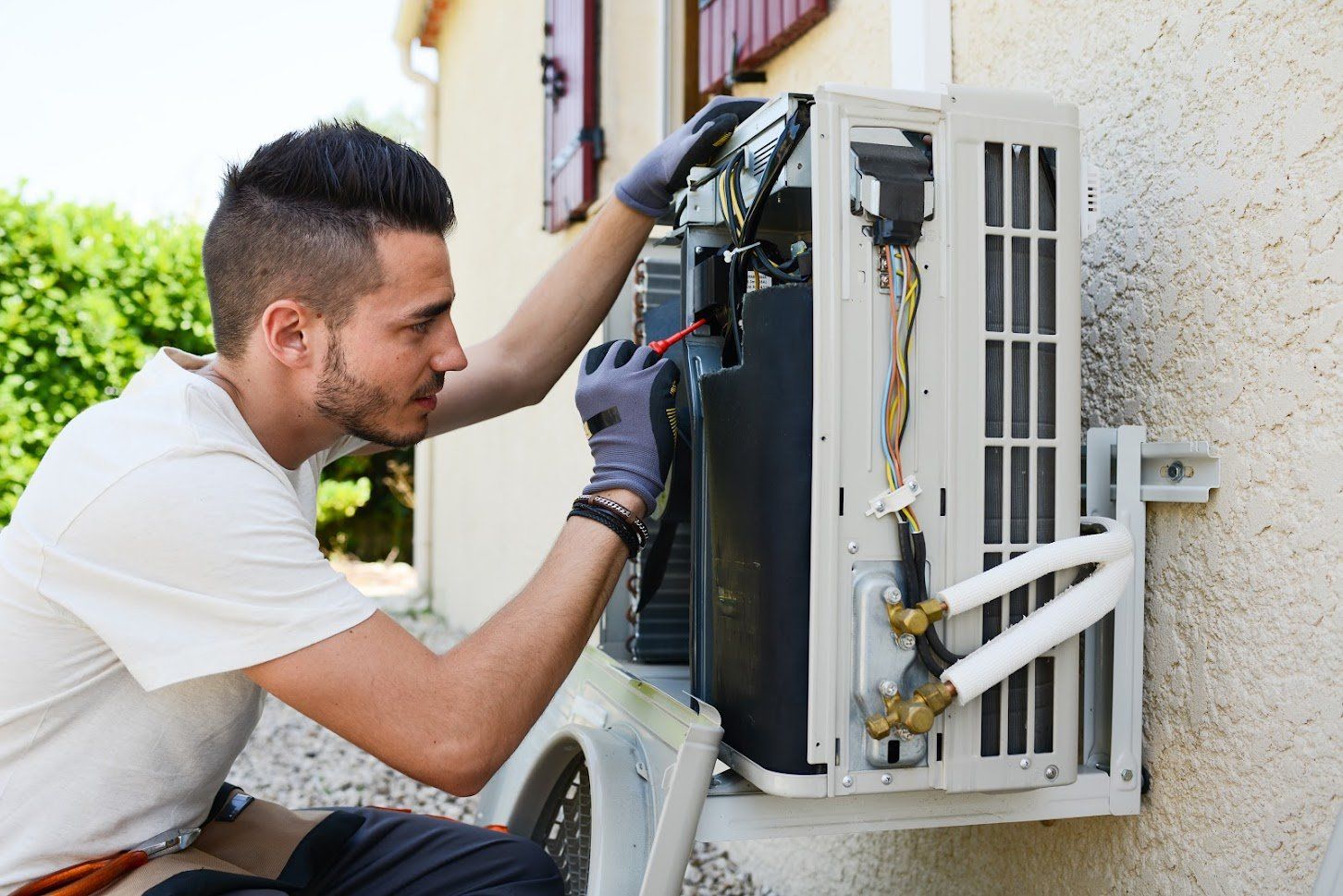
The heat exchanger separates the combustion chamber from the air you breathe. The heat exchanger ensures that heat, and not flue gases, reach your indoor air. A conventional or non-condensing furnace has a single heat exchanger. Unfortunately, such a furnace loses some heat up the chimney along with byproducts of combustion, such as combustion fumes and water vapor.
A condensing furnace, a type of high-efficiency furnace, has two heat exchangers. The second heat exchanger receives and condenses hot water vapor from the combustion process. The water vapor releases its heat as it condenses. The extra heat also warms the house, thereby enhancing the furnace's overall efficiency.